In April 2024, global energy and technology provider Hitachi Energy announced a substantial US$1.5 billion investment to enhance global transformer production by 2027. This led to a IDTechEx discussion by technology analyst Mika Takahashi about hydrogen fuel cells and grid upgrades that will revamp EV charging.
According to IDTechEx’s research into electrical grids, transformers are vital components and potential supply bottlenecks for large-scale grid upgrades, which are critical as society transitions from a petrochemical-fuelled transportation sector to one powered by electricity.
The market report, Off-Grid Charging For Electric Vehicles 2024-2034: Technologies, Benchmarking, Players and Forecasts, highlights the challenges utility grids face amid the electrification of vehicles.
Restructuring ageing utility grids, initially built for centralised coal power distribution, to accommodate increasing renewable energy generation and electric vehicle adoption, presents a significant challenge that industry and policymakers are beginning to address.
Hitachi Energy's investment includes the construction of a new factory in Finland, aimed at reducing the current lengthy wait times—over two years in the US—for transformers. These devices are essential for stepping down high-voltage transmission lines to usable voltages for end customers.
However, some locations, such as temporary sites, festivals or remote industrial locations, may remain beyond the reach of grid and mains electricity. For these scenarios, distributed generation is necessary.
Diesel generators, the incumbent technology, are increasingly seen as polluting and face potential bans in inner-city construction sites due to air and noise pollution regulations. Furthermore, charging ‘green’ electric construction vehicles with diesel generators contradicts environmental goals.
Research indicates that hydrogen fuel cell generators stand out as a promising alternative for green on-site power generation, suitable for construction and temporary power needs.
Repurposing the fuel cell for distributed generation
Fuel cell technology, initially pioneered in early space programs, is gaining renewed interest as a solution for distributed power generation. While Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) were once seen as a promising alternative to Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) due to faster refueling and greater range, sales figures indicate that BEVs are significantly outperforming FCEVs.
IDTechEx forecasts that fully battery electric vehicles will become the dominant net-zero drivetrain.
Despite this, the fuel cell generator sector is experiencing growing momentum. These generators repurpose fuel cell technology to produce electricity from hydrogen. By combining hydrogen with oxygen from the air, fuel cell generators produce electricity and water with zero carbon emissions and significantly reduced noise compared to diesel generators.
Unlike solar and wind systems, which require on-site batteries, fuel cell generators use stored energy in the form of compressed hydrogen. This allows for scalable power output by increasing the fuel cell stack size, enabling the charging of large electric construction vehicles or multiple conventional vehicles.
These generators promise clean, non-intermittent, and scalable power.
IDTechEx research highlights the use of fuel cell generators in electric construction sites, festivals, remote electric vehicle races, and public highway fast charging stations. Hitachi Energy is among the latest companies to invest in hydrogen fuel cell generators, a sector that IDTechEx predicts will generate over US$14 billion by 2034.
The challenge is affordable and green hydrogen
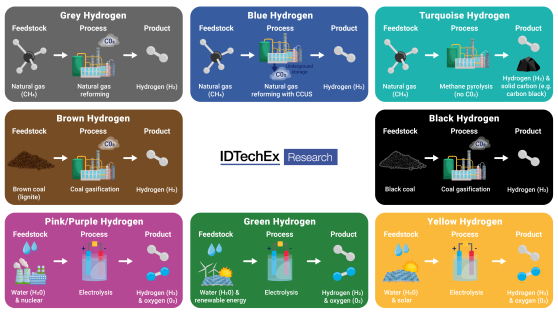
The allure of carbon-free on-site electricity is compelling, but a comprehensive evaluation of emissions requires considering the entire supply chain, particularly the method or ‘colour’ of hydrogen (H2) production.
Hydrogen colours denote production methods, with only green and yellow hydrogen being truly renewable. If grey or black hydrogen is used, hydrogen generators merely shift emissions from the point of use to the source of production, offering no substantial reduction in overall emissions. Conversely, using green, renewable hydrogen significantly reduces overall emissions. The critical question is whether operators will opt for green or grey hydrogen, largely dependent on cost and availability.
Currently, green hydrogen is considerably more expensive due to its production inefficiency—around 3 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of input renewable energy yields 1 kWh equivalent of H2. For commercial operators, operational expenditure (OPEX) considerations are paramount, and the high cost of green hydrogen makes it unlikely they will pay a substantial premium.
Availability is another hurdle, as present green hydrogen production is limited and region-specific. The research reveals that some hydrogen fuel cell generator companies have had to produce their own green hydrogen to meet customer demand, as external suppliers cannot provide the necessary quantities.
The IDTechEx report, “Off-Grid Charging For Electric Vehicles 2024-2034: Technologies, Benchmarking, Players and Forecasts”, quantitatively assesses these challenges and offers market intelligence on the growing fuel cell generator market and utility grid challenges.
The report also examines the quantities of green hydrogen needed to power the electric construction industry, identified as a key application for fuel cell generators. Forecasts are detailed by generator size and region, providing granular insights into this emerging market.
Read more on Proactive Investors AU