It can be hard work to build your savings over time. It doesn’t just come down to how much you’re putting away after each pay check - although we all know the higher, the better. The interest rate also plays a pretty big part as the higher the rate, the faster your hard-earned savings will grow.
As long as you let the bank know your tax file number (TFN). While this isn’t mandatory by any means, choosing not to provide your TFN could see you pay withholding tax on your interest earnings.
Huh?
Here’s a debrief on what withholding tax is and what you can do to avoid paying it. Plus, a breakdown of paying tax on interest earned from a savings account.
What is withholding tax on a savings account?
When you open a savings account, your bank will give you the option of providing your TFN. While it’s not compulsory, supplying your TFN can be beneficial in the long run.
If you choose not to provide your TFN, the bank is required by law to automatically withhold a certain amount from the interest that you earn annually and transfer it to the Australian Taxation Office (ATO).
Withholding tax on a savings account is calculated at the top marginal tax rate of 45% with the additional Medicare levy of 2.5%. Withholding tax also applies to non-residents of Australia as well, and for them, the tax rate is 10%.
If you forgot to supply your TFN, it’s not the end of the world. You can claim a tax credit for any withholding tax when you lodge your tax return. However, keep in mind that you earn interest on top of your interest (compounding returns). So the more interest you have in your account, the more you will earn!
You do not need to pay withholding tax if:
-
You are under 16 years of age and the account earns less than $420 in interest each year
-
You are over 16 years of age and the account earns less than $120 in interest each year
Which savings accounts are affected by withholding tax?
According to the ATO’s ‘refund of tax file number amounts deducted’ form, you can claim a refund of amounts from any of the following investment bodies: your bank, building society, credit union, or company in which you own shares or unit trust. This includes accounts such as term deposits and savings accounts.
Do you pay tax on interest from a savings account?
When you file your income tax return at the end of each financial year, you need to declare all your sources of income. This includes the interest you have earned on your savings. When lodging your tax return, you’ll need to declare the amount of interest earned (not the whole balance of your savings account) and pay tax on it at your standard income tax rate.
But why do you need to declare it?
Under the ATO’s rules regarding investment income, all Australian residents are required to declare any interest they receive as income. You’ve earned that money in a similar way to earning your salary or wage.
At what rate is the interest taxed?
The amount of tax that applies to the interest you earn on a savings account will be determined by your overall taxable income. The ATO’s tax rates for the 2023-24 financial year are below:
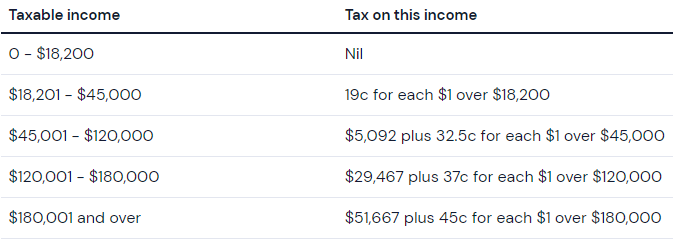
Here is an example to consider:
John’s income for the financial year was $70,000. Plus, he also earned $2,500 in interest on his high-interest savings account. This interest would be added to John’s total income, meaning he’d have a taxable income of $72,500. He will be taxed 32.5% of the $2,500 ($812.5) since his taxable income falls in the $45,001-$120,000 bracket.
How do I report the interest earned?
If you’re planning to lodge your tax return online via myGov, there will be a section on income earned through bank accounts and investments. In most cases, this will already be pre-filled for you as banks and other financial institutions are required to report to the ATO details of the interest they pay to account holders and investors.
If the box is not pre-filled, you can find how much interest you have earned for the financial year on an annual bank statement and then enter the amount yourself. Make sure this figure is accurate as the ATO will match it with the investment income reported by your bank. If any inconsistencies are found, your tax return may be adjusted and fines could apply.
What about interest earned on a children’s savings account?
If you have opened a savings account for your child, but you spend the money in the account for your own day to day purchases, then you must declare any interest earned in your own tax return.
However, if the funds deposited into the account are the child’s own money - say, birthday or Christmas presents, pocket money, or money earned from a part-time job - the interest earned is classified as the child’s income.
If the child has no other source of income other than the interest earned, and it comes to less than $420 for the financial year, the child is not required to file an income tax return. If the child is under 16 and the interest earned exceeds $420, they will need to lodge a tax return.
See Also: Which banks offer the highest interest kids savings accounts?
What about interest earned on a joint account?
In terms of joint accounts, the ATO assumes that joint account holders are equal owners of an account and requires them to pay tax accordingly. For instance, if you have a joint account with your partner, the interest paid will be split equally. When filing your tax returns, each account holder must declare their 50% share of interest earned which is then added to their taxable income.
In the case that ownership is not shared equally, the ATO will require documentation to prove this. This must show the source of the money, the proportion of contributions from each account holder, who uses the funds in the account most, and the interest earned.
"What is withholding tax on a savings account?" was originally published on Savings.com.au and was republished with permission.
