Preclinical data from a study assessing Patrys Ltd (ASX:PAB)’s full-size IgG deoxymab PATDX3 has revealed the antibody platform is capable of enacting a ‘synthetic lethality’ mechanism in cancer cells, essentially destroying them from the inside out.
The deoxymabs platform has a number of novel properties not typically found in antibodies – one of these is the ability to enter a cell and cell nucleus and block the DNA Damage Response (DDR) systems.
These systems are usually responsible for protecting normal cells and preventing cancer-causing mutations.
In tumours where these systems have already been damaged, PAT-DX3’s additional inhibition effect can cause an accumulation of DNA damage that ultimately kills the tumour cells.
This approach is known as 'synthetic lethality' and has been successfully used to treat certain tumours with several new small molecule cancer drugs.
New potential markets
“This is an exciting and important result that shows for the first time the comparative effects of a Patrys deoxymab on tumours with or without DDR mutations in the same animal,” Patrys CEO and managing director Dr James Campbell said.
“This study was requested by a potential partner as part of Patrys’ ongoing business development activities.
“This study confirms the potential to use deoxymabs as a single agent to treat cancers which have pre-existing mutations that compromise their DDR systems, including BRCA2 negative breast cancer and other cancers.
“In addition, Patrys is looking at using deoxymabs in combination with DNA damaging therapies, such as radiation and chemotherapies, and as a delivery agent for small molecules and nucleic acids.”
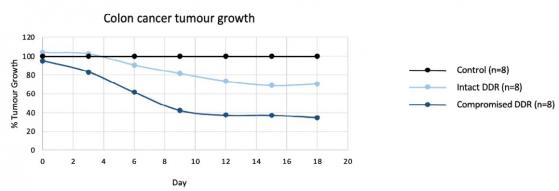
Graph representing comparative effects of deoxymabs on tumours with or without DDR mutations in the same animal.
In a pre-clinical colon cancer study in mice treated with PAT-DX3, tumours with a compromised DDR system showed a 71% reduction in growth, significantly more than the 35% reduction in growth in tumours with an intact DDR mechanism.
Patrys said this result provided further evidence of a synthetic lethality mode of action for Patrys’ deoxymabs platform – a first for therapeutic antibodies.
Read more on Proactive Investors AU